

Dec. 31, 2025
Pet skin itching has become one of the most common health issues plaguing pet owners, affecting the quality of life of both pets and their human companions. Recent statistics show that over 40% of veterinary clinic visits are related to skin problems, with itching being the primary complaint. Understanding the symptoms and adopting proper treatment measures is crucial for safeguarding the health of furry friends.
Pets with skin itching often exhibit obvious abnormal behaviors. The most typical signs include frequent scratching with paws, rubbing their bodies against furniture or walls, and excessive licking of specific areas such as paws, abdomen, and ears. In severe cases, hair loss, redness, swelling, scabs, or even oozing lesions may occur on the skin. Some pets may also experience restlessness, loss of appetite, or weight loss due to persistent discomfort.
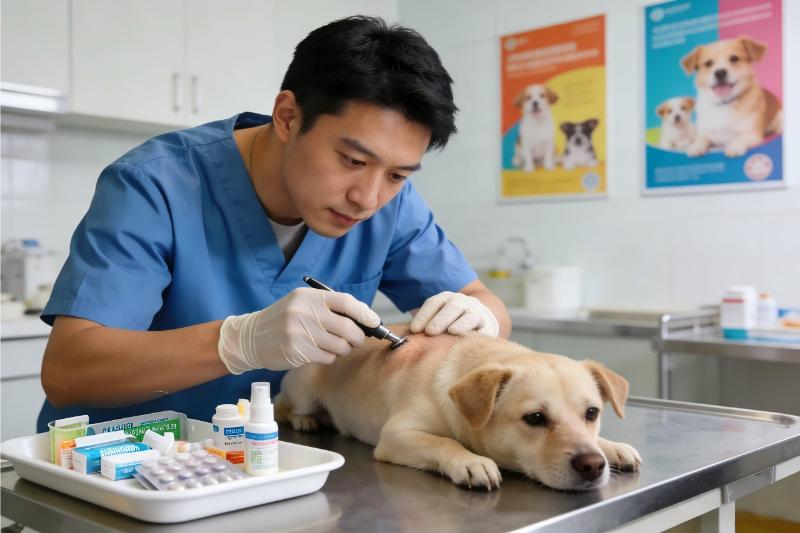

The first step in treating pet skin itching is to identify the root cause, which may include allergies (food, pollen, mites), parasitic infections (fleas, ticks), fungal or bacterial infections, or underlying health conditions. It is recommended that pet owners take their pets to a professional veterinarian for a comprehensive examination, such as skin scraping tests or allergy screenings, to determine the exact cause.
Based on the diagnosis, veterinarians will formulate targeted treatment plans. For allergic reactions, anti-allergy medications or hypoallergenic diets may be prescribed. Parasitic infections require the use of safe and effective deworming products. When it comes to fungal infections, terbinafine hydrochloride tablets and sprays are commonly recommended. For the tablets, the dosage should be determined by the pet’s weight, usually administered once daily with food for 3 to 7 consecutive days. For the spray, shake well before use, spray directly on the affected skin 2 to 3 times a day, and avoid letting the pet lick the area for 10 minutes after application. Bacterial infections, on the other hand, need corresponding antibiotics. Additionally, regular grooming, maintaining a clean living environment for pets, and avoiding the use of irritating cleaning products can help prevent skin itching.
Veterinarians emphasize that even with over-the-counter options like terbinafine hydrochloride preparations, pet owners should consult a vet first to confirm fungal infection and get the correct dosage. Never arbitrarily use human medications or adjust the dosage of pet drugs, as this may exacerbate the condition or cause side effects. Timely medical intervention and scientific care are the keys to helping pets recover from skin itching and maintaining their long-term health.